Recently, hair loss in women had a big moment: At the 2022 Oscars, comedian Chris Rock made a joke about actress Jada Pinkett Smith's bald head - and earned a slap in the face from her husband Will Smith. Suddenly, the whole world knew the technical term for hair loss: alopecia.
NOT JUST A MEN'S PROBLEM: HAIR LOSS ALSO AFFECTS WOMEN
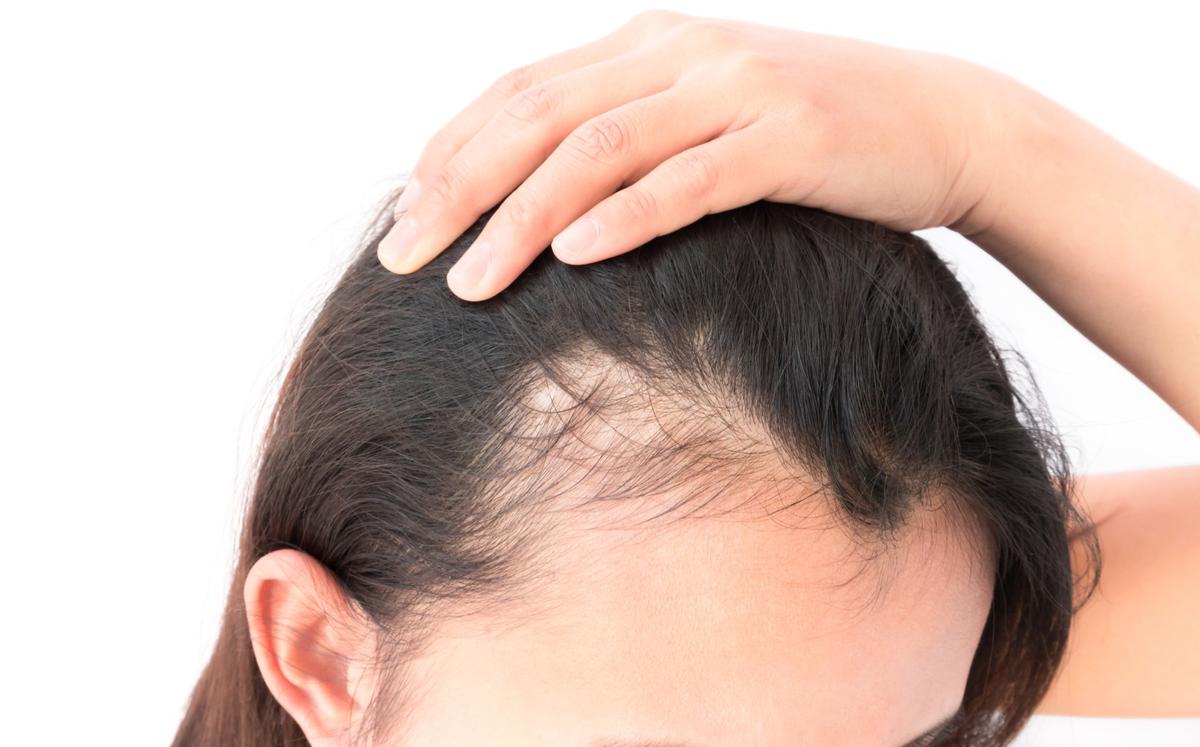
Men with thinning hair or baldness are commonplace. The fact that women also suffer from hair loss has so far been taboo. However, around 50 percent of all women are affected by hair loss over the course of their lives.
Women with bald heads rarely appear in public - like Jada Pinkett Smith, who suffers from alopecia areata. Hair is very important to women and the topic of hair loss scares many. If more hair than usual appears in the brush, on the pillow or in the sink, it can be an important signal.
Up to 100 hairs fall out every day - that's completely normal. After hair falls out, the hair follicles produce a new hair again. However, if more than 100 hairs fall out every day, the hair generally appears thinner or the scalp is visible, there may be something wrong with your health. In this case, it is advisable to go to the doctor (dermatologist). The earlier hair loss is diagnosed and the cause identified, the more likely treatment will be successful.
WHAT ARE THE CAUSES OF HAIR LOSS IN WOMEN?
The general term for thinning hair with visible scalp or bald patches is alopecia. Doctors distinguish between over ten different types of hair loss. Each type can have different causes.
Hereditary hair loss (androgenetic alopecia or AGA) is the most common form of hair loss and is noticeable in women through thinning of the head hair. The cause is a genetic predisposition, so hair loss is hereditary.

Alopecia areata or circular hair loss leads to circular bald patches. Outside of these bald patches, hair grows normally. The cause is an autoimmune reaction (autoimmune disease).
Diffuse hair loss is diagnosed when the hair on the head falls out evenly and the entire head of hair appears thinner. The causes are varied and include stress, hormonal fluctuations (e.g. due to pregnancy or menopause), anemia or deficiencies such as iron deficiency due to an unbalanced diet, medications (e.g. beta-blockers, blood thinners, cholesterol-lowering drugs, hormonal contraceptives, retinoids and drugs for ADHD, thyroid diseases and narcolepsy), acute illnesses such as infections, Covid or syphilis as well as chronic illnesses (such as anorexia, bulimia, diabetes mellitus, lupus or Crohn's disease) and poisoning (e.g. due to ionizing radiation, pesticides or the metal thallium).
A special form is hair loss after pregnancy. A drop in estrogen levels can lead to diffuse hair loss around two to four months after birth. The temples and hairline are particularly affected. This hair loss is usually temporary and the hair grows back normally after some time (between six weeks and a maximum of 15 months).

WHICH NUTRIENTS AND VITAMINS ARE MISSING IN WOMEN WITH HAIR LOSS?
Hair needs certain nutrients to grow and look healthy and shiny. If these nutrients are missing or present in insufficient quantities, hair grows finer and can break off more quickly or fall out prematurely. The most important nutrients include vitamin B12, iron, folic acid and zinc. An unbalanced diet with insufficient nutrient intake can therefore lead to hair loss. In addition, stress, certain illnesses and medications can have a negative impact on nutrient absorption, so that despite a balanced diet, not enough nutrients and vitamins are absorbed in the intestine.
WHICH HORMONES ARE MISSING IN HAIR LOSS IN WOMEN?
Hair loss can be caused by hormones. A lack of hormones is usually not the cause. Rather, it is fluctuations in hormone levels that cause problems for hair. Oral contraceptives with gestagens, pregnancy with a subsequent drop in estrogen, or menopause, during which less and less estrogen is produced, are all possible causes. Androgenization (masculinization), which is genetically determined and causes hair follicles to react sensitively to male hormones (androgens such as testosterone and the resulting dehydrotestosterone (DHT)) in the female body, can also lead to hair loss.
HOW TO STOP AND TREAT HAIR LOSS IN WOMEN?
In order to stop hair loss, it must first be determined what type of hair loss it is and what the causes are. The right person to contact is a dermatologist. In the dermatological practice, the scalp is examined using a special device (trichoscan or trichogram). The condition of the scalp, the condition of the hair follicles and how easily hair can be pulled out (pluck test) are determined. The doctor will also ask about the patient's medical history, whether there are any chronic or acute illnesses or whether medication is being taken. The family history of hair loss is also discussed. A blood test can also be done to check the values for thyroid, hormones or nutrients, for example. Other tests such as hair analysis or tissue samples are possible.
A treatment may then be recommended depending on the specific type of hair loss.
In cases of hormone-related hair loss, anti-androgens are prescribed, which inhibit the effect of male hormones on the hair follicles and also promote blood circulation in the scalp.
The drug Minoxidil can be used to treat hereditary hair loss. It lowers blood pressure and can lead to stronger hair growth.
In the case of circular hair loss, the active ingredients dithranol and cortisone can help when applied locally to the bald area.
Another treatment option is hair transplantation.
WHICH HAIR CARE FOR HAIR LOSS IN WOMEN?
Anyone suffering from hair loss should treat their hair and scalp with care. This includes a mild shampoo, such as the Balance Eco Shampoo for sensitive and dry scalps. It contains no silicones or heavy care additives and is specially designed for a hypersensitive scalp. It is important to dry freshly washed hair slowly, either in the air or with a hairdryer on a mild heat setting. Brushing or combing is only permitted when the hair is two-thirds dry. When wet, the hair is particularly sensitive and can be torn out when combed or brushed.
When it comes to styling and hairstyles, less is more. Avoid heavy styling products, clips or braids and either wear your hair down or tie it loosely. Anything that pulls on your hair or weighs it down can promote hair loss.